Porkkalankatu 22
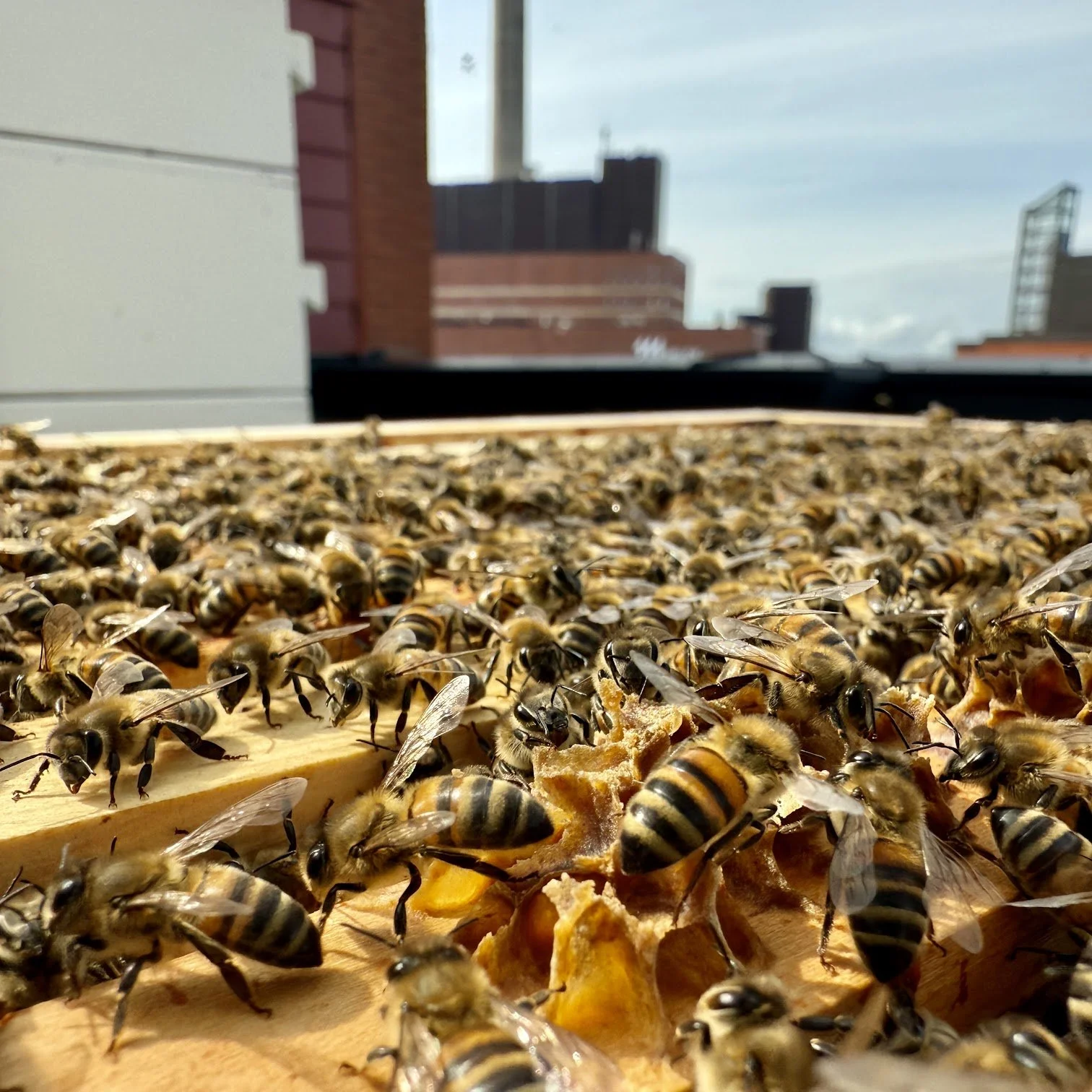
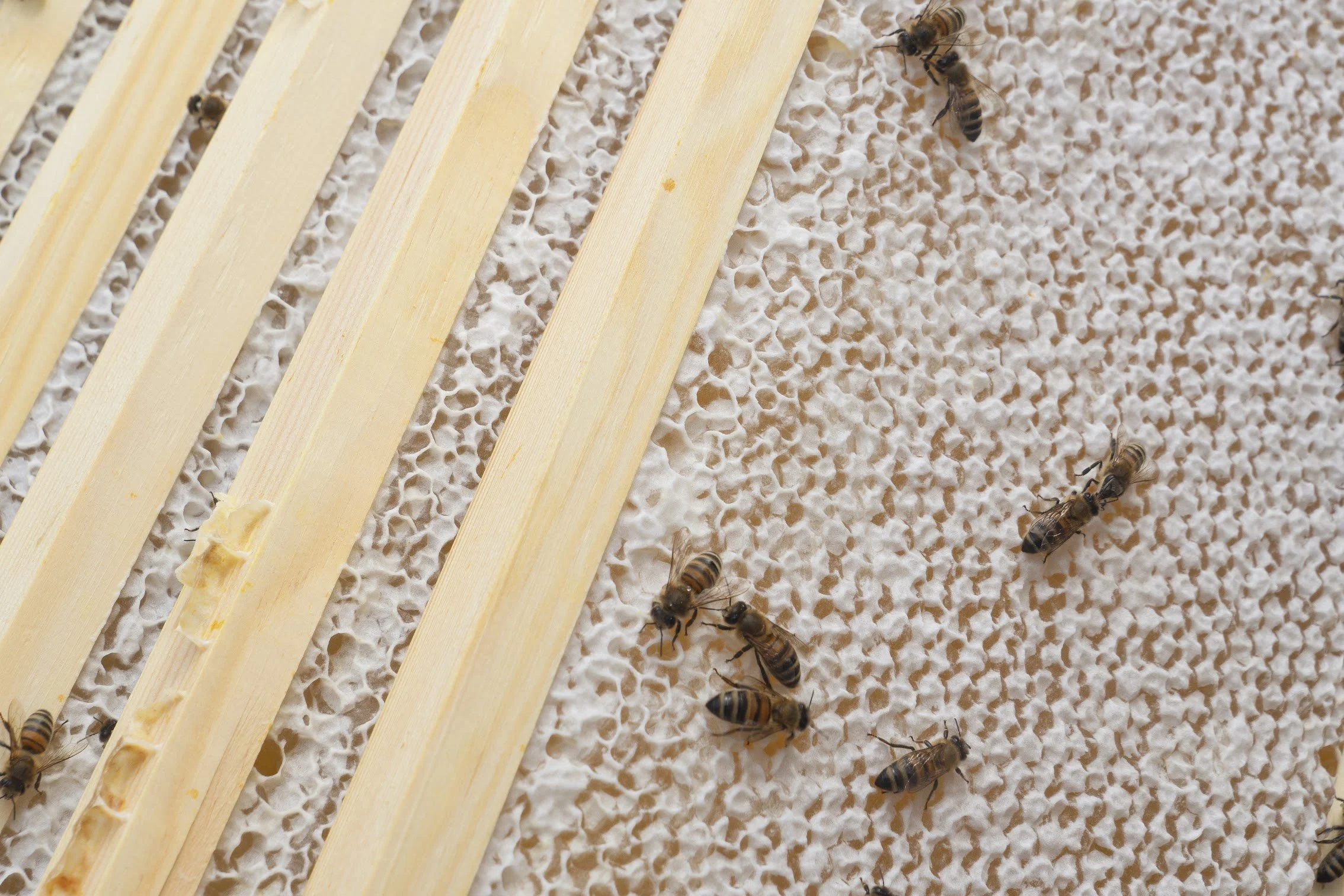
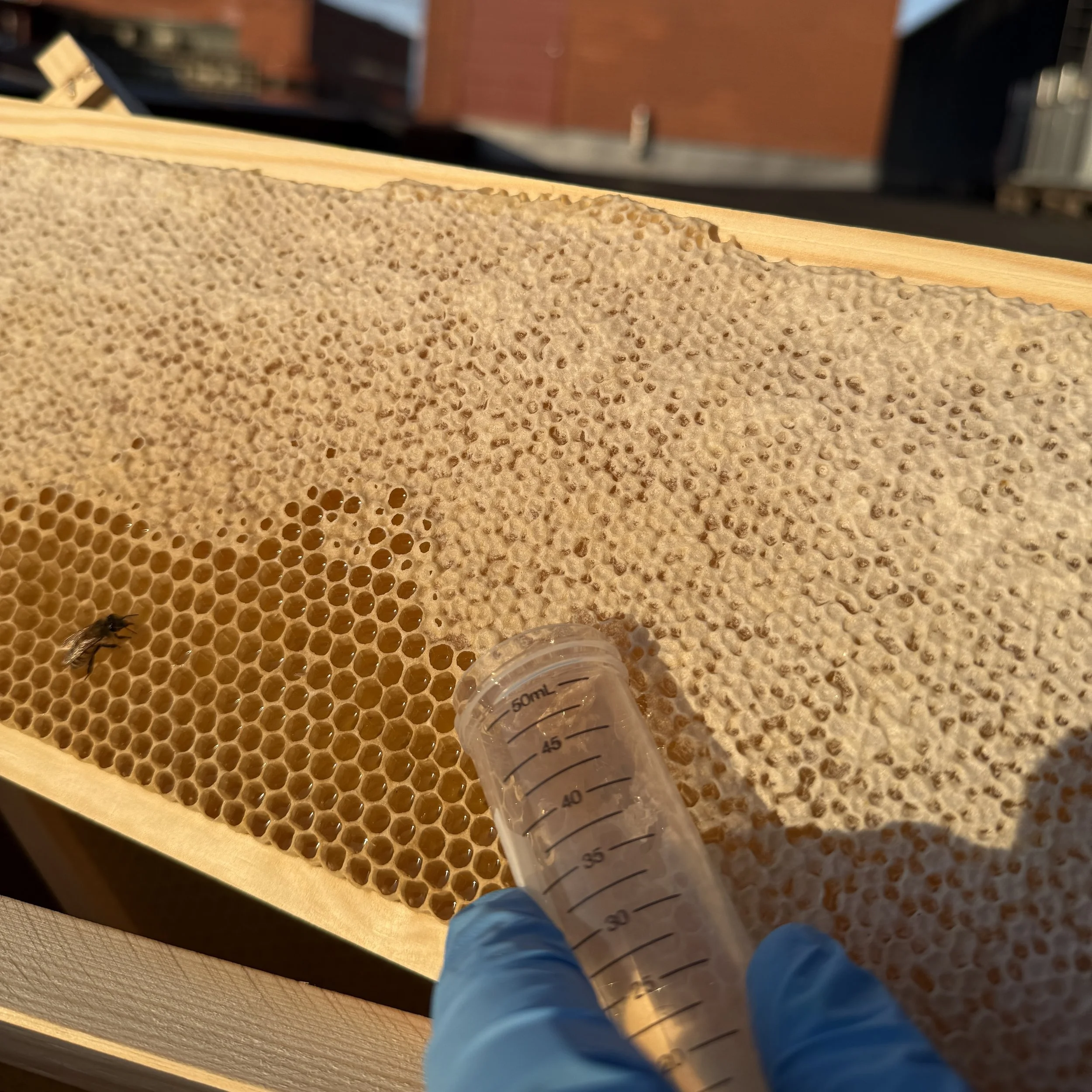
Tervetuloa Porkkalankatu 22 toimistomehiläisten omalle sivulle. Täällä voit seurata pörriäisten kuulumisia ja tutustua projektiin tarkemmin. Mehiläiset tekevät tärkeää työtä pölyttäessään lähialueen kukkivia kasveja ja samalla ne keräävät pesäänsä DNA näytteitä joiden avulla voidaan tutkia ympäröivän luonnon monimuotoisuutta.
50 000
Mehiläistä arviolta
1257 ha
Luontoa kartoitettu
Usein kysyttyjä kysymyksiä
Olemme listanneet tähän vastauksia yleisimpiin kysymyksiin pörriäisteemasta.
Kerro meille jos keksit lisää hyviä kysymyksiä!
-
Tarhamehiläiset ovat sosiaalisia hyönteisiä, jotka kuuluvat Apis-sukuun, pääasiassa Apis melliferaan. Ne elävät suurissa yhdyskunnissa, jotka koostuvat tyypillisesti tuhansista yksilöistä ja ne tunnetaan monimutkaisesta sosiaalisesta rakenteestaan sekä kyvystään tuottaa hunajaa.
-
Tarhamehiläiset ovat elintärkeitä pölyttäjiä, jotka pölyttävät noin kolmanneksen kuluttamistamme elintarvikkeista, mukaan lukien monet hedelmät, vihannekset ja pähkinät. Niiden pölytystyö on tärkeää myös luonnonkasveille jotka puolestaan tarjoavat ravintoa sekä suojaa muille hyönteisille ja eläimille.
-
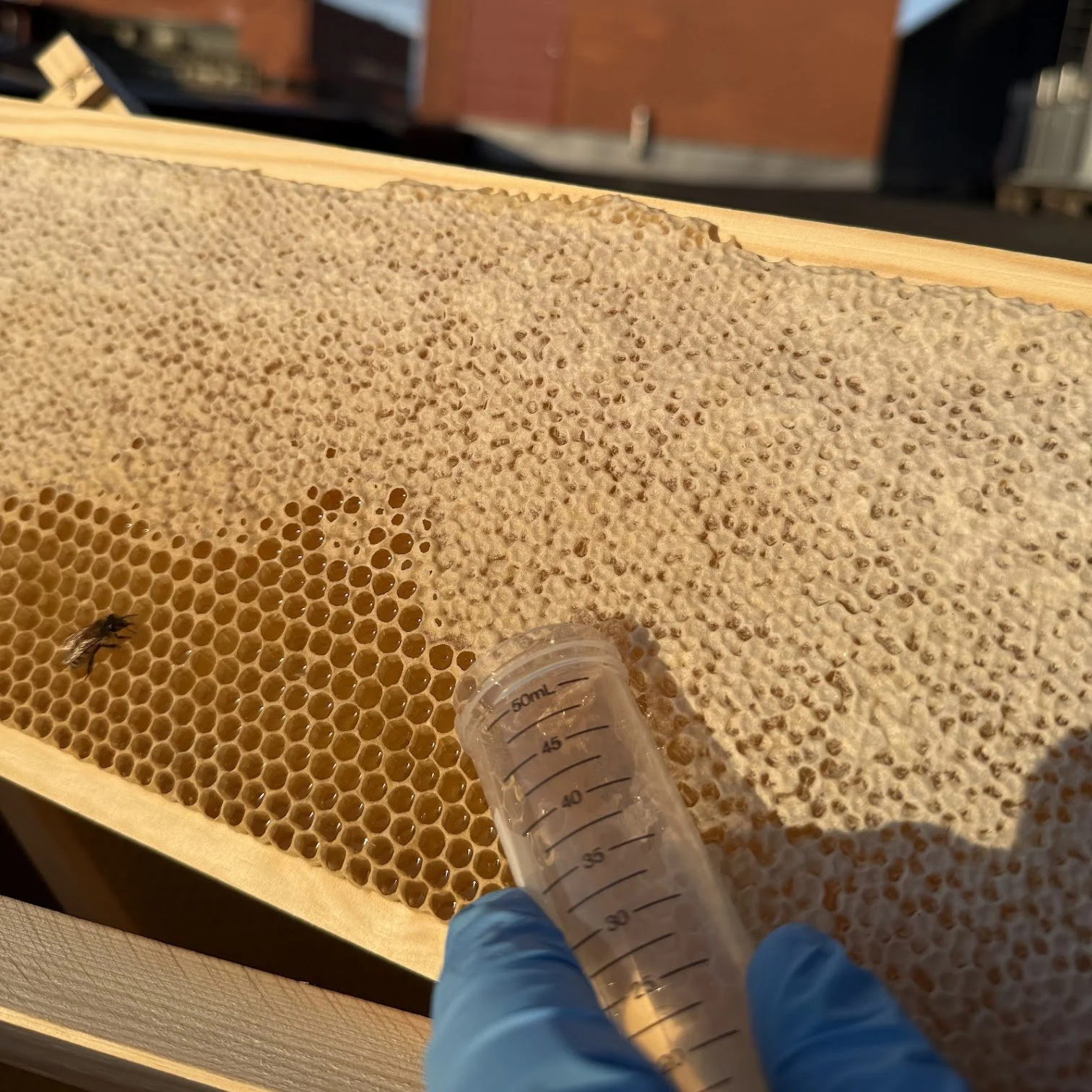
Hunajan valmistus alkaa, kun työmehiläiset keräävät kukista mettä mesimahaansa missä ne kuljettavat sen pesäänsä. Pesässä mesi siirtyy lentomehiläisiltä varastomehiläisille jotka lisäävät siihen entsyymejä ja varastoivat sen kennoihin. Sitten mehiläiset levittävät meden kuusikulmaisiin mehiläisvahakennoihin, joissa ne tuulettavat sitä siivillään vähentääkseen kosteuspitoisuutta ja muuttaakseen sen hunajaksi.
-
Mehiläiset käyttävät ravinnokseen kukista keräämäänsä mettä sekä siitepölyä. Energiaa mehiläiset saavat hiilihydraattipitoisesta medestä ja proteiinit sekä vitamiinit puolestaan siitepölystä.
-
Mehiläiset lentävät keruulennoillaan noin 2km säteellä pesänsä ympäristössä. Kun hyvä mesi-apaja löytyy, mehiläiset muodostavat suoran lentolinjan (beeline) pesän ja mesilähteen välille ja lentävät sitä edes takaisin kunnes kukinta on päättynyt. Tämän jälkeen tiedustelijamehiläiset etsivät uuden apajan jonne lentolinja siirretään.
News & articles